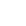Comprehensive Analysis of the Working Principle, Structural Types, and Application Fields of Check Valves
Comprehensive Analysis of the Working Principle, Structural Types, and Application Fields of
Check Valves
A check valve is a valve device that automatically opens and closes relying on the flow of the medium itself. Its core function is to prevent the reverse flow of fluid in the pipeline system. As a key component in the field of fluid control, the check valve ensures the safety and efficiency of the pipeline system through the intelligent response mechanism of the valve disc and is widely used in fields such as water conservancy, petrochemical, HVAC, and industrial production.
I. Definition and Core Function of Check Valves
A check valve opens and closes through the vertical or rotational movement of a circular valve disc. Its action completely depends on the pressure difference generated by the medium flow and the self - weight of the valve disc. When the medium flows in the forward direction, the fluid pressure pushes the valve disc to open; when the medium flows in the reverse direction, the valve disc quickly closes under the action of the reverse pressure and its self - weight. This one - way flow characteristic makes it a core component for preventing the reverse rotation of pumps, avoiding water hammer effects, and protecting pipeline equipment.
II. Core Working Principle of Check Valves
1. Forward Flow State: When the fluid flows in the forward direction, the medium pressure overcomes the self - weight of the valve disc and the resistance of the spring (if any), causing the valve disc to open and allowing the fluid to flow unimpeded.
2. Reverse Flow State: When the system pressure fluctuates or the pump stops, the pressure generated by the reverse flow of the medium and the self - weight of the valve disc act together to prompt the valve disc to close quickly, forming a physical sealing barrier.
III. Mainstream Structural Types and Performance Comparison
1. Swing Check Valves:
- It uses a hinged valve disc design and opens and closes through rotation.
- Advantages: It has a small resistance to the fluid and is suitable for large - diameter, low - pressure pipeline systems.
- Innovative technology: The newly developed soft - seated structure achieves face sealing through an inlaid sealing element, effectively improving the closing tightness and avoiding leakage problems caused by changes in medium pressure.
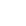
2. Lift Check Valves:
- The valve disc moves up and down along the vertical axis, and its structure is similar to that of a globe valve.
- Characteristics: It has excellent sealing performance but relatively large fluid resistance and is mostly used in high - pressure, small - diameter scenarios.
3. Wafer Check Valves:
- It has a compact design and achieves quick closing with the assistance of a spring.
- Technological breakthrough: The new anti - jamming design uses a T - shaped valve core stem and a slotted structure to ensure the stable movement path of the valve disc, completely solving the technical pain points of traditional valves, such as easy jamming and eccentricity.
IV. Technological Innovation and Industry Progress
In recent years, check valve technology has been continuously upgraded. For example:
- Anti - jamming Wafer Design: By optimizing the sliding structure of the valve core stem and the valve seat, the reliability of the valve under complex working conditions is significantly improved, and the maintenance requirements are reduced.
- Large - Diameter Soft - Sealing Solution: The design of interference - fit sealing elements and removable valve seats not only extends the service life of the sealing elements but also facilitates on - site maintenance, which is particularly suitable for the chemical and energy industries.
V. Typical Application Scenarios
1. Water Supply Systems: It prevents back - flow of water when the water pump stops, protecting the pump equipment.
2. Industrial Pipelines: It maintains the one - way flow of the medium in the transportation of oil and natural gas, avoiding mixed pollution.
3. HVAC Engineering: It controls the circulation direction of hot water in heating pipelines, improving the energy efficiency of the system.
4. Special Medium Handling: For special media such as low - moisture content powder materials, customized gate - type check valves can effectively solve the problem of easy wear of traditional valves.
VI. Selection and Maintenance Suggestions
- Selection Factors: Comprehensive evaluation should be carried out based on the medium characteristics (corrosiveness, particulate matter content), pressure rating, installation space, and flow requirements.
- Maintenance Points: Regularly check the wear of the sealing surface, clean the deposits in the valve cavity, and ensure the elastic performance of the spring. For large - diameter valves, it is recommended to use a modular valve seat structure to simplify the maintenance process.
Through continuous technological iteration and scenario adaptation, modern check valves have evolved into precision fluid control equipment with high sealing performance, strong durability, and intelligent response capabilities, providing solid support for the safe operation of pipelines in various industrial fields.