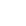
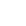Analysis of Core Advantages, Welding Techniques, and Construction Key Points of Stainless Steel Welded Air Ducts
Release time:2025-05-23 Visits:844
Analysis of Core Advantages, Welding Techniques, and Construction Key Points of Stainless Steel Welded Air Ducts
Stainless steel welded air ducts have become the ideal choice for ventilation, air - conditioning, and smoke - exhaust systems due to their characteristics such as corrosion resistance, high - temperature resistance, and strong sealing performance. This article will elaborate from aspects including their core advantages, welding techniques, manufacturing processes, and construction specifications, providing comprehensive guidance for engineering applications.
I. Core Advantages of Stainless Steel Welded Air Ducts
1. Corrosion Resistance: Made of high - quality stainless steel materials, it can resist the erosion of acidic and alkaline substances and moisture, avoiding the air pollution problem caused by rusting in traditional air ducts.
2. High Strength and Reliability: Stainless steel materials have excellent anti - deformation and anti - seismic capabilities. Combined with professional welding processes, it ensures the long - term stable operation of the pipeline in complex environments.
3. Sealing Performance: The welded joints are specially treated to reduce the risk of gas leakage, improve the system's energy efficiency, and reduce energy consumption.
4. Easy Maintenance: The smooth surface is not prone to dust accumulation, facilitating cleaning and disinfection, and is suitable for places with strict hygiene requirements such as hospitals and food processing plants.
II. Detailed Explanation of Welding Techniques
The welding methods for stainless steel welded air ducts should be selected according to the plate thickness and scene requirements:
1. Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding: Suitable for plates with a thickness of more than 1.2mm. The welds are beautiful and of stable quality, making it suitable for systems with high sealing requirements.
2. Arc Welding: Suitable for thin plates (thickness less than 1.2mm). It has high efficiency, but the current parameters need to be strictly controlled to avoid weld defects.
3. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): Using inert gas to isolate the air and reduce oxidation, it is suitable for thin - plate welding, but the operation speed is slow.
Welding Precautions:
- Thoroughly clean the plate surface before welding to remove oil and rust.
- Precisely control the current, voltage, and welding speed to avoid overheating and deformation.
- Perform pickling and passivation treatment on the welds after welding to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Operators should wear protective equipment to ensure construction safety.
III. Manufacturing Process Flow
1. Cutting and Forming: Cut the plates according to the design dimensions and use a flanging machine to complete the flanging process.
2. Assembly and Welding: Precisely align the plates, insert the reinforcement frame, and then use the appropriate welding process for fixation.
3. Reinforcement and Sealing: Use clamps to fix the transverse flanging and weld it with the reinforcement frame to improve the structural strength.
4. Surface Treatment: Pickle and passivate the welds and the pipe body to form a uniform oxide film and extend the service life.
5. Quality Inspection: Detect the sealing performance, weld strength, and appearance integrity through pressure tests, visual inspections, etc.
IV. Construction Specifications and Precautions
1. On - site Management: Keep the construction environment clean to prevent debris from entering the pipeline and affecting the air flow.
2. Installation Requirements:
- The support spacing should meet the standards to prevent the air duct from deforming due to gravity or vibration.
- The connections should be tightly aligned to reduce the risk of air leakage.
3. Acceptance Testing: After the system is installed, an air - tightness test should be carried out to ensure that the pressure loss is within the allowable range.
4. Safety Protection: Wear safety belts for high - altitude operations, and equip the welding area with fire - fighting equipment to eliminate potential safety hazards.
V. Expansion of Application Scenarios
Stainless steel welded air ducts are widely used in the following fields due to their performance advantages:
- Medical Facilities: Meeting the high - hygiene - standard requirements of clean rooms, operating rooms, etc.
- Food Industry: The corrosion - resistant material meets food - grade hygiene certifications, ensuring the safety of the production environment.
- Commercial Buildings: The central air - conditioning systems of shopping malls and office buildings, considering both efficiency and durability.
Conclusion
Through scientific material selection, precise processes, and standardized construction, stainless steel welded air ducts can significantly improve the reliability and service life of ventilation systems. In engineering practice, the welding methods and installation plans should be optimized according to the specific scene requirements to achieve the goals of high - efficiency energy conservation and long - term stable operation.