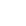
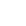A Detailed Explanation of the Core Uses and Professional Installation Methods of Galvanized Welded Air Ducts
Release time:2025-05-27 Visits:734
A Detailed Explanation of the Core Uses and Professional Installation Methods of Galvanized Welded Air Ducts
Galvanized welded air ducts are indispensable key components in building ventilation systems. With their excellent performance and wide applicability, they have become the preferred materials for ventilation projects in industrial, commercial, and civil fields. The following provides a detailed explanation from two aspects: core uses and installation specifications.
I. Core Uses of Galvanized Welded Air Ducts
1. Efficient Ventilation and Air Circulation
Galvanized welded air ducts are mainly used for the directional transportation and circulation of air inside and outside buildings. For example, in air - conditioning systems, they are used to adjust indoor temperature and humidity, or in production workshops to remove harmful gases. Their application scenarios cover grain processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, the electronics industry, shopping malls, hotels, office buildings, etc. They are especially suitable for the air - supply and exhaust systems in fire - fighting smoke - exhaust and civil air - defense projects.
2. Excellent Corrosion Resistance and Durability
The galvanized layer on the surface of the air duct can effectively isolate oxygen and moisture, preventing the steel from oxidizing and rusting, thus extending its service life. This characteristic enables it to maintain stable performance in humid, high - temperature, or chemically polluted environments, such as the steam environment in food processing plants or the corrosive gas emission scenarios in chemical workshops.
3. High Strength and Fire - proof Safety
The rigid structure of the galvanized steel plate itself gives the air duct good pressure - bearing capacity, allowing it to withstand the airflow impact of medium - and high - pressure systems. At the same time, the galvanized material has flame - retardant properties, which can effectively delay the spread of fire and provide safety protection for the fire - fighting smoke - exhaust system.
4. Energy - saving, Environmental - friendly, and Low - noise
The smooth inner wall design of the air duct reduces air flow resistance and lowers ventilation energy consumption. In addition, the reasonable structural design can effectively control noise transmission and improve the comfort of the indoor environment.
II. Professional Installation Methods of Galvanized Welded Air Ducts
1. Production and Installation Specifications of Supports and Hangers
- Material Selection and Processing: Supports and hangers should be made of angle steel and suspension rods of corresponding specifications according to the size of the air duct and the load - bearing requirements. The length of the suspension rod needs to be accurately calculated based on the installation height and the building structure (such as the position of the beam), and the threads at the end should meet the height - adjustment requirements.
- Anti - rust Treatment: All metal components need to undergo double anti - rust treatment (anti - rust paint + top - coat) to ensure that they do not rust during long - term use.
- Control of Installation Spacing: The spacing of supports and hangers must strictly follow the design specifications. For example, in the low - pressure system, when the side length of the air duct ≤ 400mm, the spacing between the air duct supports should not exceed 4m; when the side length > 400mm, it should not exceed 3m.
2. Lifting Process and Quality Control of Air Ducts
- Pre - installation Preparation: Before lifting, it is necessary to check the number, size, and system layout of the air ducts, clean the internal debris, and ensure that the connection parts are free from deformation or damage.
- Segmented Lifting Technology: Adopt segmented lifting. First, install the main pipes close to the building girders, and arrange the branch pipes as high as possible. During the lifting process, use balancing devices to prevent the air ducts from tilting and avoid conflicts with water and electricity pipelines.
- Connection and Fixation: Connect the air ducts using common - plate flanges or angle - steel flanges, and combine with sealing strips to ensure air tightness. When fixing, use angle - steel cross - bars to lock with the supports and hangers, and check the horizontal and vertical deviations (usually required to be ≤ 3‰).
- System Acceptance: After the installation is completed, a leakage - air volume test should be carried out. The leakage - air rate of the low - pressure system should be ≤ 6%, and that of the medium - pressure system should be ≤ 2%. At the same time, check the stability of the supports and the linkage function of components such as fire dampers.
III. Notes on Selection and Construction
- Selection of Plate Thickness: Select the thickness of the galvanized steel plate according to the system pressure level. For example, for low - pressure air ducts with a side length ≤ 320mm, 0.5mm plates can be used, while for high - pressure systems, the thickness should be ≥ 1.5mm.
- Optimization of Factory Prefabrication: 80% of the processes (such as cutting, forming, and sealing) can be completed by factory automated equipment, which can not only improve accuracy but also reduce on - site construction time.
- Coordination of Cross - operations: It is necessary to cooperate with professional teams in water and electricity, fire - fighting, etc. Complete the installation of air ducts first and then install the ceiling panels to avoid rework.
Through scientific material selection and standardized construction, galvanized welded air ducts can significantly improve the efficiency of the ventilation system and reduce operation and maintenance costs. They are an ideal solution for modern building ventilation projects.